While artificial intelligence technology is already in use in telephone answering systems with speech recognition and in popular household gadgets like the iRobot vacuum cleaner, none of the existing systems have been as ambitious as Darpa's Grand Challenge road race.N.B. Probability theory is essential. But it's not the whole story. And probability theory may not be the only coherent and effective mathematical strategy for dealing with uncertainty and shades of gray.This leap was possible, in large part, because researchers are moving from an approach that relied principally on logic and rule-based systems to more probability or statistics-oriented software technologies.
"In the past A.I. has been dominated by symbolic systems and now the world is gray," said Terrence J. Sejnowski, head of the computational neurobiology laboratory at the Salk Institute in La Jolla, Calif. "That's what it's like to deal with the real world."
Friday, October 14, 2005
Probabilistic Computational Intelligence: The World Is Gray, Not Black and White
Wednesday, October 12, 2005
Canine Personality, Canine Character, Canine Science & Canine Value
3. Defendant's motion to preclude all testimony and exhibits that seek to attribute human qualities or attributes to plaintiff's dogThe issue to be tried is whether defendant's actions on April 8, 1998, violated plaintiffs' constitutional and state law rights. Evidence that would seek to attribute human characteristics to the dog is not relevant and will be excluded.
The pictures attached to defendant's motion must be examined under a Rule 403 analysis. The first picture, of the parking lot at the location of the incident, is clearly admissible. The picture of the dog and the child on the couch with the child thinking "we're best buddies" is excluded under Rule 403. The third picture attached to the motion shows one of plaintiffs' children leaning on the dog, who is [lying] on the floor. It is admissible because it is evidence of how well behaved the dog was with people and is not unfairly prejudicial to the defendant. The fourth picture shows the dog by herself wearing a large bow around her neck. Unless the dog was wearing this collar when shot on April 8, 1998, the picture is excluded under Rule 403.
4. Defendant's motion in limine to preclude all character testimony related to plaintiff's dog
Plaintiffs seek to introduce testimony establishing the friendly nature of their dog in an attempt to refute defendant's claim that she lunged at him. Defendant argues that such testimony is inadmissible character evidence under Federal Rule of Evidence 404.
We have not found any Pennsylvania or Third Circuit cases addressing whether evidence of past behavior of an animal should be excluded under Rule 404, however, the highest courts of several states have admitted such evidence. See Hood v. Hagler, 1979 OK 163, 606 P.2d 548, 551-52 (Okla. 1979); Forsythe v. Kluckhohn, 161 Iowa 267, 271, 142 N.W. 225 (Iowa 1913); Stone v. Pendleton, 21 R.I. 332, 43 A. 643, 643-44 (R.I. 1899); see also 1A Wigmore, Evidence § 68a (Tillers rev. 1983). I will not exclude evidence concerning Immi's disposition as inadmissible character evidence.
...
8. Defendant's motion in limine to preclude the expert report of Andrew Bensing
Plaintiffs seek to have Andrew Bensing testify as an expert on the behavior of Rottweilers. He would testify to the behavior of female Rottweilers as a breed and the behavior of Immi in particular. Defendant challenges the testimony on three grounds: (1) that it would be inadmissible character evidence; (2) that Mr. Bensing's experience with the dog would be irrelevant because it ended over a year before the shooting; and (3) that it does not satisfy the prong of the Daubert analysis that requires a "fit" between the expert testimony and the facts of the case.
The objection to the testimony as inadmissible character evidence is taken care of by my ruling on character testimony in general. Testimony about Immi's past behavior is admissible.
That Mr. Bensing's frequent contact with the dog ended a year before the incident does not render his testimony irrelevant. Mr. Bensing had extended contact with Immi for over two years and then occasional contact with her until her death. Defendant may point out to the jury that Mr. Bensing's time with the dog was only occasional for a year before her death, but he cannot preclude his testimony entirely.
Defendant's argument about the "fit" step of the Daubert analysis will be considered at a Daubert hearing.
9. Defendant's motion in limine to limit testimony regarding the valuation of plaintiff's dog
Under Pennsylvania law a dog is personal property. 3 P.S. § 459-601 (2002); Desanctis v. Pritchard, 2002 PA Super 221, 803 A.2d 230, 232 (Pa. Super. 2002) 3 P.S. § 459-601 (2002). It is proper as regards the section 1983 claim, therefore, to limit testimony regarding the value of the dog to that addressing its value as a piece of personal property. No testimony regarding the value of Immi to the plaintiffs in particular will be admitted as evidence regarding the valuation of the dog.
Sunday, October 09, 2005
Imprecise Language and Imprecise Perceptions
 Consider the following statement by Professor Lotfi Zadeh in his recent abstract Computation with Information Described in Natural Language—The Concept of Generalized-Constraint-Based Computation (October 5, 2005):
Consider the following statement by Professor Lotfi Zadeh in his recent abstract Computation with Information Described in Natural Language—The Concept of Generalized-Constraint-Based Computation (October 5, 2005):Computation with information described in natural language cannot be dealt with through the use of machinery of natural language processing. The problem is semantic imprecision of natural languages. More specifically, a natural language is basically a system for describing perceptions. Perceptions are intrinsically imprecise, reflecting the bounded ability of sensory organs, and ultimately the brain, to resolve detail and store information. Semantic imprecision of natural languages is a concomitant of imprecision of perceptions.Legal theorists, students of legal reasoning, and aficionados of factual inference in legal settings: What say you?
Deprivation of US & NJ Right of Confrontation because Trial Court Barred Defense from Cross-Examining Prosecution Witness about Polygraph Test Results
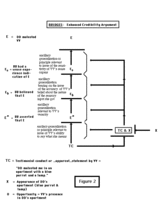 State v. Castagna, 376 N.J. Super. 323, 870 A.2d 653 (April 12, 2005), cert. granted, 185 N.J. 35, 878 A.2d 852, (July 7, 2005):
State v. Castagna, 376 N.J. Super. 323, 870 A.2d 653 (April 12, 2005), cert. granted, 185 N.J. 35, 878 A.2d 852, (July 7, 2005):Our decision to reverse is based on an erroneous legal ruling that operated to deprive all three defendants of their right to confront the witnesses against them, as guaranteed by the Sixth Amendment of the Constitution of the United States, as applied to the states by the provisions of the Fourteenth Amendment, and as independently embodied in Article I, Paragraph 10 of the New Jersey Constitution. This constitutional deprivation came about when the trial court precluded defense counsel from cross-examining a key prosecution witness on the results of a stipulated polygraph examination, because these defendants were not parties to the stipulation.We hold that when the State enters into an agreement with a witness, stipulating to the admissibility of the results of that witness's polygraph examination, a defendant has a constitutional right to confront that witness, in cross-examination, with the results of the polygraph, as a means of impeaching that witness's credibility. As a matter of fundamental fairness, we also hold that, under these circumstances, the State is precluded from disavowing the reliability of the polygraph results.
